Services
![[12:03] Ranjith Kumar Pillai Chronic Kidney Disease [12:03] Ranjith Kumar Pillai Chronic Kidney Disease](https://joysivadasansantha.whitecoats.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/47/elementor/thumbs/image-qo8hkcvnihf0hslhhmu5n9finokyy1lw3ssarjdfw8.png)
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where kidneys gradually lose function, leading to waste buildup in the blood. Common causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, and glomerulonephritis. Symptoms may not appear until later stages. Treatment aims to slow progression and manage complications, potentially including dialysis or kidney transplant.
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is a sudden decline in kidney function due to illness, injury, or medication. It can lead to electrolyte imbalances, fluid overload, and accumulation of waste in the body. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications and may involve addressing underlying causes and supportive care like dialysis.

Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic Nephropathy is kidney damage resulting from prolonged high blood sugar levels in diabetes. It progresses slowly, impairing kidney function and potentially leading to kidney failure. Treatment involves controlling blood sugar and blood pressure, along with medications to slow progression. Early detection and management are vital to prevent complications.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is kidney inflammation affecting glomeruli, the kidney's filtering units, often due to immune system issues or infections. It can lead to proteinuria, hematuria, and impaired kidney function. Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms, but severe cases may progress to chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis or transplant.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder causing fluid-filled cysts to develop in the kidneys, impacting their function. Symptoms include pain, high blood pressure, and urinary tract infections. PKD can lead to kidney failure. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications, with options like medication, cyst drainage, or kidney transplant.
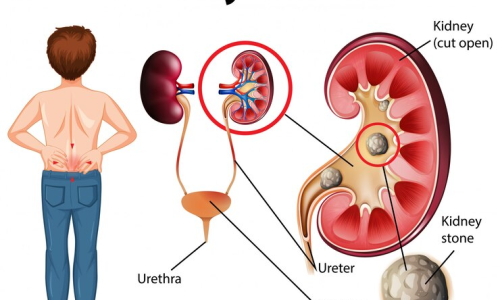
Kidney Stones
Kidney Stones are hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys, causing intense pain as they pass through the urinary tract. Common types include calcium, uric acid, and struvite stones. Treatment may involve pain management, increased fluid intake, and in severe cases, procedures like lithotripsy or surgery to remove the stones.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephrotic Syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by high levels of protein in urine, low levels of protein in blood, swelling, and high cholesterol. It can result from various underlying conditions, including kidney diseases. Treatment aims to reduce proteinuria, control symptoms, and address the underlying cause through medications and dietary changes.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer, originating in the lining of the kidney tubules. Symptoms may include blood in urine, flank pain, and a palpable mass. Treatment options include surgery, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation, depending on the stage and individual patient factors. Early detection improves prognosis.

Hematuria
Hematuria is a medical condition characterized by the presence of blood in the urine. It can be caused by various factors, including urinary tract infections, kidney stones, or kidney injury. While sometimes symptomless, it may indicate underlying health issues. Diagnosis involves medical evaluation, including imaging tests and urine analysis. Treatment targets the underlying cause.
